Relapsed/Refractory International Prognostic Index (R/R‐IPI): An international prognostic calculator for relapsed/refractory diffuse large B‐cell lymphoma - Maurer - 2021 - American Journal of Hematology - Wiley Online Library

CNS International Prognostic Index: A Risk Model for CNS Relapse in Patients With Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma Treated With R-CHOP | Journal of Clinical Oncology

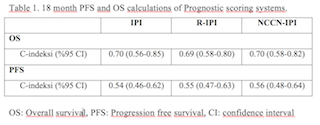
The revised International Prognostic Index (R-IPI) is a better predictor of outcome than the standard IPI for patients with diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. - ppt download
A New Prognostic Score for Elderly Patients with Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma Treated with R-CHOP: The Prognostic Role of Blood Monocyte and Lymphocyte Counts Is Absent | PLOS ONE

The revised International Prognostic Index (R-IPI) is a better predictor of outcome than the standard IPI for patients with diffuse large B-cell lymphoma treated with R-CHOP - ScienceDirect
Differential Impact of Relative Dose-Intensity Reductions in Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma Treated with R-CHOP21 or R-CHOP14 | PLOS ONE

MYC and BCL-2 adjusted-International Prognostic Index (A-IPI) is a better predictor of outcome than the standard IPI for patients with diffuse large B-cell lymphoma treated with R-CHOP. | Semantic Scholar

Prognostic impact of MYD88 mutation, proliferative index and cell origin in diffuse large B cell lymphoma | Hematology, Transfusion and Cell Therapy

The international staging system improves the IPI risk stratification in patients with diffuse large B-cell lymphoma treated with R-CHOP | Scientific Reports

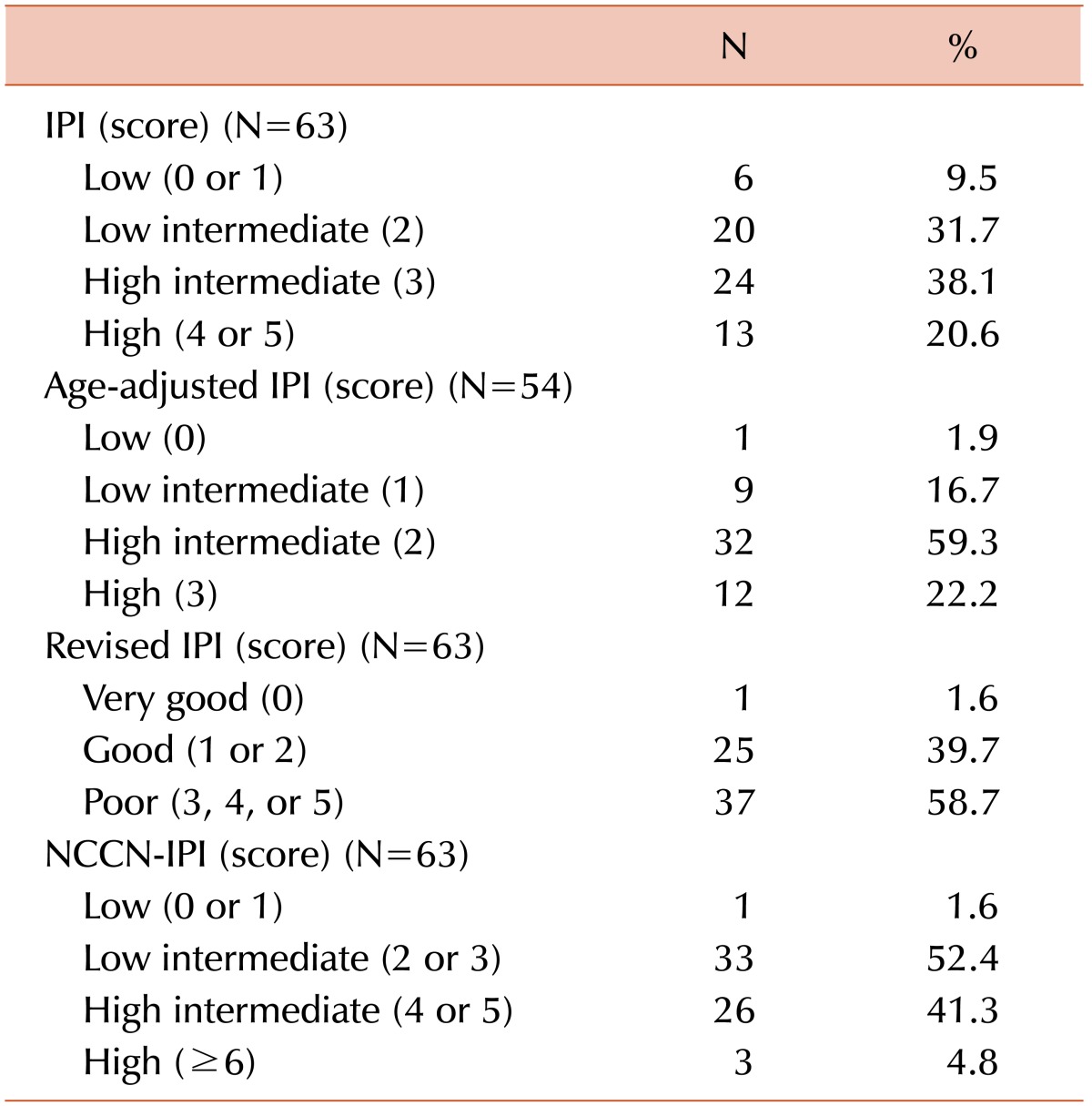
Table 1 from An enhanced International Prognostic Index (NCCN-IPI) for patients with diffuse large B-cell lymphoma treated in the rituximab era. | Semantic Scholar

Modified Number of Extranodal Involved Sites as a Prognosticator in R-CHOP-Treated Patients with Disseminated Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma

Revised International Prognostic Index (R-IPI) Is a Better Predictor of Outcome Than the Standard IPI for Patients with Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma (DLBCL) Treated with Rituximab and CHOP (R-CHOP). - ScienceDirect

Outcome according to the revised International Prognostic Index (R-IPI)... | Download Scientific Diagram
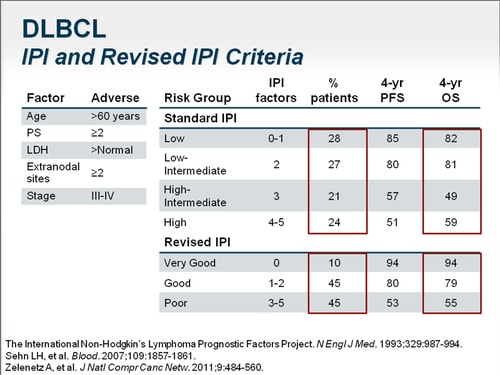
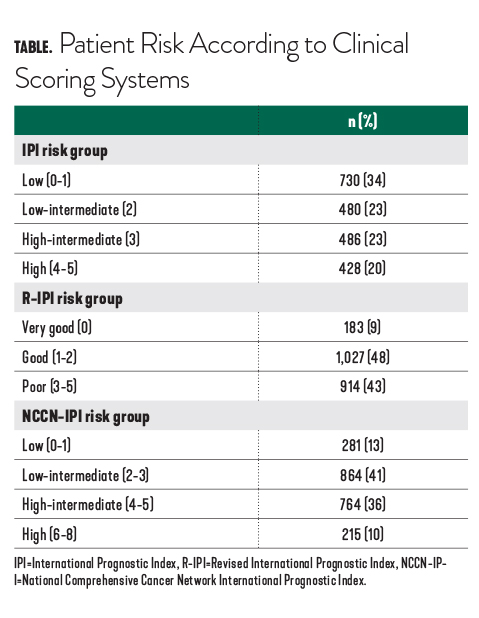
![Distribution of patients inside risk groups and OS by standard IPI [8],... | Download Table Distribution of patients inside risk groups and OS by standard IPI [8],... | Download Table](https://www.researchgate.net/profile/Santo-Neri/publication/38095873/figure/tbl1/AS:667607128604690@1536181351880/Distribution-of-patients-inside-risk-groups-and-OS-by-standard-IPI-8-R-IPI-3-and_Q640.jpg)